Trademark Registration in India
What is Trademark Registration in India?
Trademark registration in India permits the applicant to use symbols or words to symbolize a business or the items offered by a business in order to identify their goods or services from competitors. Once a trademark is registered in India, no other organization may use it for as long as it is in use.
Once the trademark is registered, the “TM” symbol can be used with the trademark applicant and the brand. Trademark registration is an asset for the firm, and it is required to register for trademark registration in India in order to preserve the brand name. It is usually preferable to seek trademark registration in Bangalore under the supervision of a professional because the process consists of several phases that must be completed and also necessitates ongoing follow-up from the government.
Eligibility for Trademark Registration in India
Trademark registrations are commonly used to protect unique brands, slogans, or invented terms. Individuals, corporations, and non-profit organizations can all apply for trademark registration in India. However, each of the several classes of persons or entities has separate requirements for filing a trademark application. The following items are eligible for trademark registration in India.
- An individual
An individual who is not in business can also file a trademark application and receive trademark registration for a symbol or word that the applicant intends to use in the future.
- Joint owners
If two people decide to file a trademark application, both of their names must be included on the application.
- Proprietorship Firms
When filing a trademark application in India for a sole proprietorship firm, the applicant’s entire name must be included. The proprietorship or the business name is not suitable.
- Partnership Firm
When filing a trademark application for a partnership firm, the names of all the partners should be included. If the partnership firm contains a minor, the name of the guardian who is representing the minor must be mentioned.
- Limited Liability Partnership
In the event of a Limited Liability Partnership, the application should be made in the LLP’s name. An LLP is a legal entity in which the partners each have their own identity. Because the trademark belongs to the LLP, the partners cannot be the applicant.
- Indian Company
When a Private Limited Company, a Person Company, or a Public Limited Company applies for trademark registration, the application must be made in the name of the company. They cannot be applied by the Director because they are all independent established entities. It can, however, be signed and filed by the Director or any officer approved by the officer.
- Foreign Company
If a foreign incorporated entity applies for a trademark in India, the application must be made in the corporate name as it is registered in the foreign nation. The nature of the registration, the country, and the law should all be indicated here.
- Trust or Society
If a trademark application is lodged on behalf of a trust or a society, the name of the managing trustee, chairman, or secretary representing the trust or society must be specified.
Types of Trademark Registration in India
Product marks, service marks, collective marks, certification marks, shape marks, sound marks, collective marks, certification marks, shape marks, sound marks, and pattern markings can all be registered. Though there are different trademarks, their objective is the same: to allow consumers to identify the items and services created by certain manufacturers or service providers. Let us look at the several sorts of trademark registrations in India.
- Product mark
Product Identification, a product mark is applied to a good or a product as opposed to a service. A product mark assists in identifying the origin of the goods and in protecting the business’s reputation. Trademark applications filed under the trademark 1-34 may be classified as product marks because they represent goods.
- Service mark
Service Logo, a service mark is comparable to a product mark in that it represents a service rather than a product. The primary function of the service mark is to distinguish the proprietors from the owners of other similar services. The trademark applications are submitted under trademark classes 35-45, which might be considered a service mark because they represent services.
- Collective mark
Mark Collective, the collective mark informs the audience about the distinct characteristics of the products and services used to represent a collective. This mark can be used by a group of people to collectively protect the goods and services. The mark holder may be an association, a public institution, or a Section 8 company.
- Certification mark
Mark of Certification It is a label that indicates the product’s origin, material, quality, or other specific information provided by the proprietor. The primary goal of certification is to raise the level of the product while also ensuring the product’s quality to customers by demonstrating that the product has completed standard tests to ensure quality. Certification marks are commonly found on packaged goods, toys, and electronics.
- Shape mark
The form mark is solely used to protect the shape of a product so that customers associate it with a specific manufacturer and choose to purchase the goods. Once it is determined that the product has a shape, the shape can be registered.
- Pattern mark
Pattern markings are used for products that have a specifically designed pattern that serves as the product’s distinguishing feature. Patterns that do not stand out as exceptional marks are rejected. A pattern mark must be distinct in order to be registered.
- Sound mark
A sound mark is a sound that is associated with a product or service that comes from a specific supplier. Sound logos, often known as audio mnemonics, appear at the opening and finish of commercials. The melody for the Indian Premier League is the most popular sound mark in India.
Documents required:
Trademark registration in India is a procedure that should be carried out with the assistance of a professional. Chhota CFO has assisted over 50,000 trademark applicants in registering their trademarks.
The following documents are required for trademark registration:
- Identity proof of the trademark owner
- PAN
- Aadhar Card
- Certificate of Incorporation ( In case of a Private Limited Company or an LLP)
- Udyog Aadhar Registration
- Logo if it is applicable and available
- Address proof
Procedure:
Benefits
There are numerous reasons to obtain a trademark registration, but the majority of them are required for all companies and aspiring entrepreneurs because it serves as a significant asset for the company. There are numerous benefits to obtaining a trademark registration and using the services. Here are a few benefits.
- Intellectual Property Protection
Trademark registration provides legal protection against the unauthorized use or reproduction of the company’s name or registered logo. The trademark owner acquires ownership of the trademark, which can be legally enforced in any court. By registering a trademark, the owner gains nationwide ownership of the mark, which can be legally enforced in any court.
A trademark registration serves as an official notice that the trademark is already registered.
- Powerful Deterrent
A trademark owner obtains the right to publicly market the brand as a registered trademark, which notifies others and prevents innocent infringement defenses. Once a trademark is registered, it will appear in search reports, discouraging other applicants from pursuing registration of the same or similar mark.
If you are the first to register a trademark, the National Trademark Office in New Delhi will deny registration to any trademark that appears to be confusingly similar to another such trademark.
- Legal remedies
By registering a trademark in India, the trademark owner can claim up to threefold damages from the infringer. The owner is presumed to be the rightful owner of the mark. By registering a trademark, the owner gains the right to sue anyone who is misusing the mark in any court. An unregistered trademark, on the other hand, is vulnerable to lawsuits.
Crucial points
Trademark registration is now possible online thanks to technology improvements. Thousands of businesses in India have benefited from the services of Chhota CFO.
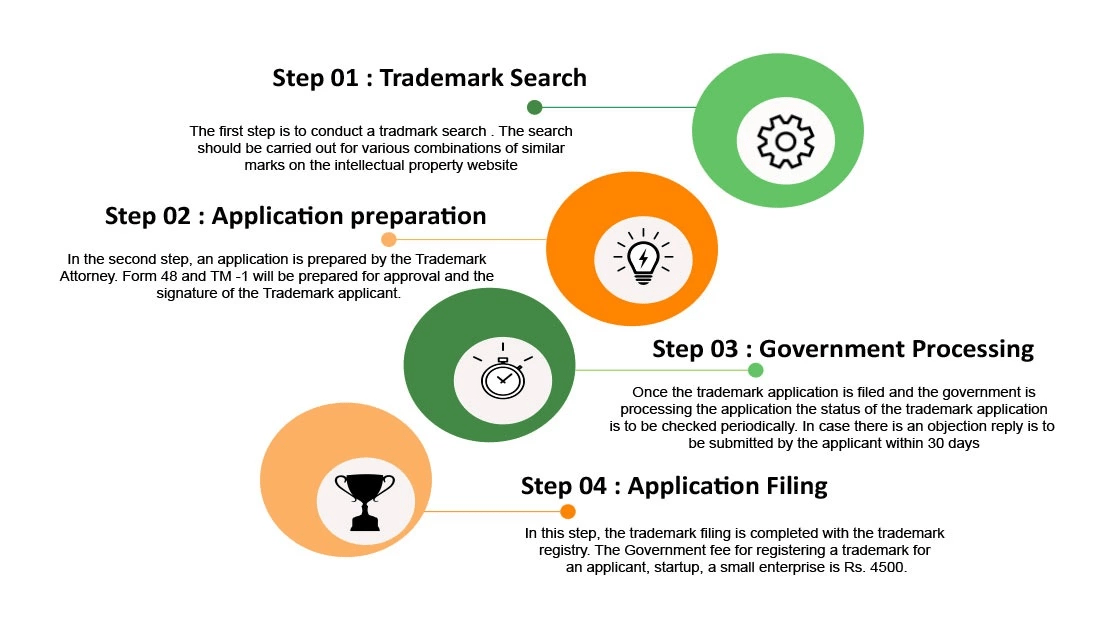
- Trademark Search
Trademark Search: Prior to beginning, the entrepreneur needs to conduct a trademark availability search. A Trademark search will reveal information on identical or similar Trademarks that have been filed with the Trademark Registry. How Do You Conduct Trademark Research? Will do the same for you.
- Trademark filing
The trademark registration application can be filed with the Trademark Registrar after the trademark search is completed. However, the application must be done in the required manner and accompanied by the applicable fees. The application can be made online or at any of the state’s five Trademark Registrar’s offices. To register a trademark online, go to the Chhota CFO’s website.
The following information must be included in the Trademark Registration application:
- The Trademark or the Logo
- Trademark holder’s name and address
- Use of a trademark Because of the date
- Product or service description
- The Vienna Codification Process
The Vienna Classification, often known as the Vienna Codification, is an international classification of the symbolic aspects of trademarks that were established by the Vienna Agreement (1973). Following the filing of the Trademark registration application, the Trademark Registrar will apply the Vienna classification to the Trademark based on the figurative aspects of the mark. While this work is being done, the trademark application status is normally “Sent for Vienna Codification.”
- Trademark Examination
Following the completion of Vienna Codification, the Trademark registration application will be assigned to an officer in the Trademark Registrar’s office. After that, the officer will analyse the Trademark application for accuracy and produce a Trademark examination report. The officer has the authority to accept the Trademark application, enable trademark journal publication, or object to the Trademark registration process.
If the application is denied, the applicant may appear in front of the Trademark officer to address the objections. If the officer deems the justification satisfactory, the Trademark will be approved for publishing in the Trademark journal. If the applicant’s reasons are not sufficient, he or she has the right to appeal.
- Trademark Journal Publication
The proposed Trademark is published in the Trademark journal once the Trademark Registrar accepts registration application. This magazine is issued weekly and contains all of the trademarks received by the Registrar. Furthermore, the public may oppose the Trademark Registration if they believe it would harm them. If no objections are received within 90 days of publication, the mark will be registered within 12 weeks.
If a third party objects to the application, the Trademark Hearing Officer will schedule a hearing. Both the applicant and the opposer have the opportunity to appear and present their respective justifications. The Trademark Hearing Officer will decide whether the application should be accepted or rejected based on the hearings and evidence presented. The decision of the Hearing officer, however, might be disputed by the escalating officer.
- Trademark Registration
If no objections or oppositions are filed, simply the trademark document and registration will be prepared and granted. Only once the Trademark registration Certificate is issued is the Trademark deemed to be the owner’s registered trademark, allowing the owner some exclusive rights to the mark. The ® Symbol can now be added to a logo or a trademark.
Summary:
A trademark can be registered for any term, name, device, label, numerals, or color combination that can be represented visually.
The proposed trademark must also be distinctive for the services or goods for which it is intended to be registered.

