Shareholders Agreement services in Bangalore
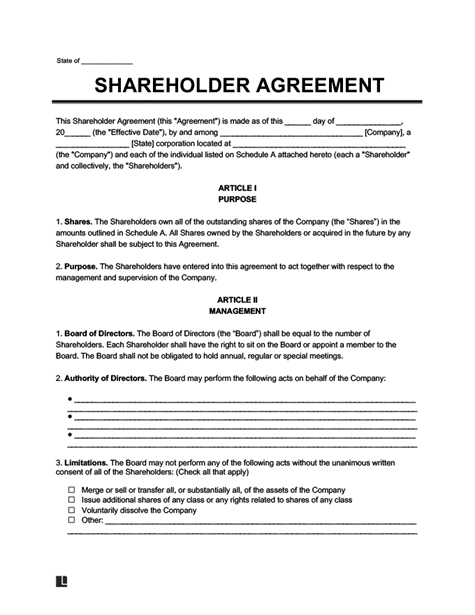
Welcome to Chhota CFO Shareholders’ agreement services in Bangalore. A shareholders’ agreement is a crucial document that outlines the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of shareholders in a company. Whether you’re starting a new venture or restructuring an existing business, having a well-drafted shareholders’ agreement is essential to protect the interests of all parties involved.
The purpose of a shareholders’ agreement is to regulate the relationships, rights, and obligations of all the company’s shareholders as well as the day-to-day operations of the business.
Shareholder agreements are not particularly governed by law in Spain. It does not need to be registered at the company registry or in front of any other official office for it to exist or be valid. However, most of the time the parties choose to have one to produce a more official and secure document to sign in front of a notary.
The type of project or business we are regulating will determine the specifics of shareholders’ agreements. It can address a range of topics, including daily operations and organization processes, corporate endeavours, and shareholder connections.
It is significant to keep in mind that shareholders’ agreements are separate contracts, making them a different kind of document that can coexist with a company’s articles of association.

The fundamental rights and duties arising out of the firm are outlined in the shareholders agreement. It establishes how the company’s members relate to the business. Members and the company sign into this type of agreement to specify their fundamental rights and obligations.
A start up path resembles a roller coaster in many ways. The future is uncertain, and many significant changes may take place within the first two or three years of the business for a variety of reasons.
A shareholders’ agreement is crucial because you can use it to anticipate specific circumstances that might adversely influence the development or expansion of the business. A shareholders’ agreement will control how an issue can be addressed and what steps must be taken to solve it, even though it is true that it won’t prevent a problem on its own.
The shareholders’ agreement’s main purpose, whether it be for founders or investors, is to establish the ground rules for all parties participating in the business. How to accomplish this the aim is to get to a mutually binding agreement that will need to be written into a legal instrument.
To ensure that the agreement is legitimate and enforceable, it is crucial to specify not only the rules but also the obligations and rights that each party will be given. It is crucial to have legal counsel from an authority on these issues.
TYPES OF SHAREHOLDERS AGREEMENT
- Seed stages
At the seed stage, the shareholders’ agreement will primarily serve to control the fundamental aspects of the founders’ relationship, starting with their ownership stakes, contributions, obligations and roles, their loyalty to the business, vesting rules, etc. Even before the firm is formed, the founders might negotiate and execute this kind of shareholders agreement.
- Early stages
At this stage, start-ups often have been around for a while, thus a shareholder’s agreement can include the objectives as well as additional ones, such as those that apply when a new founder joins the business or receives funding from early-stage investors. At this point, two things could occur:
- A shareholder’s agreement that was previously in place for the business will need to be changed because of the new founder or investment.
- It will be required to govern all parties’ interactions as well as incorporate control or economic clauses for the investor because the company lacked a shareholders’ agreement.
- Growth stages
Companies in the growth stage have typically already discovered product/market fit and verified their business models, but they still require a significant cash infusion to expand quickly and solidify their position. The negotiation of an investment agreement, which will serve as the new shareholders’ agreement between all parties involved in the operation, will now be led by experienced VC investors.
PRINCIPAL PROVISIONS OF SHAREHOLDERS AGREEMENT
The specific circumstances in which a shareholders’ agreement is drafted will determine the clauses to include however, the following are the key clauses, broken down by group:
- General Clauses: Like any agreement, it must state the objective of the document, any prior agreements between the parties, their respective roles, the term of the contract, and the applicable law and jurisdiction.
- Operational and organizational clauses: These are the terms that govern the company’s legal structure, the appointment of directors and their authority, the contributions of the shareholders, the duties, and responsibilities of each party, as well as dedication, obligations, and vesting.
- Clauses pertaining to shareholder rights and obligations: Here, we should lay out the decision-making procedure, the format for the shareholders’ meeting, the voting procedures, and the compensation for the company’s founders or important collaborators. Agreements regarding the treatment or investment of the firms’ future advantages may also be included.
- Protection clauses: Examples of this type of clause include founders’ promises, vesting requirements, non-compete agreements, and non-disclosure terms. It is crucial to incorporate any provisions that would guarantee the enforcement of all the agreements and anticipate any impasse situations and how to resolve them.
- Exit clauses: such as drag-and-tag-along clauses, buy-out provisions, and others, will govern the financial terms of any future investments in the company or exits.
PROCEDURES OF SHAREHOLDERS AGREEMENT
The creation of a shareholders agreement requires considerable thinking and effort. Before creating this type of agreement, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the rights and associated obligations.
It is essential to seek the advice or legal experts before drafting a shareholders’ agreement. Give us information so we can create the shareholders agreement. Following that, we will begin preparing the agreement.
We would get in touch with you if more information about the shareholders agreement was needed. We will send you the shareholders agreement after we have completed the first draft. If any changes were to be made or additions needed to be made, they would be made.
ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS AGREEMENT CONTAINS
- Shares are sold
One of the key clauses that should be present in a shareholder’s agreement is this one. The sale and transfer of shares would be an example. Shares could only be sold or transferred with the parties’ respective consent.
- Conditions for the Business
The shareholders agreement would discuss and consider any business-related requirements. This will cover the company’s financial needs, potential sources of finance, and any need for initial start-up money.
- Conditions for Meetings
In a firm, there are two different sorts of meetings: board meetings and general meetings. These meetings’ quorums must be in accordance with the 2013 Companies Act. In accordance with the meetings, the consent of the respective shareholders must also be decided.
- Assessment of Shares
The way firm shares are valued will affect the evaluation criteria. Here, the evaluation type is considered. Whether the market approach, the income approach, or any other approach, such the asset approach, is used for evaluation.
- Amounts Owed by Shareholders
The obligation of the members would typically only extend to a certain amount of unpaid capital on the firm’s shares if the company were a private limited company. The corporation’s liability would typically be restricted if it were a private limited or public limited company. The firm’s separate legal existence is where the concept of shareholder liability originates.
- Rights of Minority Shareholders
Rights of minority shareholders pertain to the company. Compared to majority shareholders, minority shareholders possess a smaller percentage of the company’s shares. Minority shareholders’ rights may be applicable in the following situations:
- Inform the Board of any instances of oppression and poor management pertaining to corporate affairs.
- To file a class action lawsuit against the company’s auditors and directors
- Minority shareholders have the right to request that the majority shareholders sell their stake.
CONCLUSION
A shareholder agreement serves as a framework to defend the business’s interests and shield it from harm. Every Shareholder Agreement shall contain the essential terms and provisions necessary to achieve the balance between the interests of the shareholders and the Company.
Either before or after the firm is created, a SHA can be reached. However, it is advised that the founding team finish the SHA before forming the firm and obtain legal counsel. Business attorneys are familiar with the relevant contract editors and can inform business owners of the specific details that need to be controlled in each scenario.
A SHA, in our opinion, is a crucial control tool for shareholders of start-ups and SMEs, and its significance in conflict situations shouldn’t under any circumstances be understated. The SHA establishes clear guidelines for the future in addition to offering legal stability.

